| CAS
NO. |
1758-73-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
217-157-8;
224-065-1 |
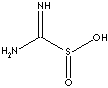
| FORMULA |
H2NC(=NH)SO2H |
| MOL
WT. |
108.11 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2925.29.9000 |
| TOXICITY |
Mouse LD (Ora): > 600mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
Formamidine sulfinic acid;
FAS; Thiourea S,S-dioxide; |
|
Aminoimino
methanesulfinic acid;
Formamidinsulfins urea;
Thioharnstoffdioxid; Aminoiminomethansulfins ure;
Aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid; Aminoiminomethansulfinsäure (German); ácido aminoiminometanosulfinico (Spanish);
Acide aminoiminomethanesulfinique (French); Other RN: 4189-44-0; 23056-93-1;
42580-06-3; 56766-73-5; 110445-04-0; 852937-99-6; |
|
SMILES
|
C([S@@](O)=O)(N)=N |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
Reducing agent.
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white powder |
| MELTING POINT |
126
C (Decomposes) |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.68
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
soluble (max 27 g/l) |
| pH |
4 at 10 g/l |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Decomposes
on exposure to light and if heated |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
|
|
Thiourea dioxide
is a strong reductant. This product is used in leather processing industry,
paper, pulp and board industry,
photographic industry,
textile processing industry,
bleaching and reducing agents. This product is also a component of decolorisation agents.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/
The use of thiourea dioxide as reducing agent in the
application of sulphur dyes:
Thiourea dioxide was applied as reducing agent during the dyeing of
cellulosic fibres with eight commercial sulphur dyes. The same dyes were also
applied frow dyebaths containing sodium sulphide. It was found that the
intensity and fastness properties of the dyeings by both methods were similar,
although in some cases slight differences in shade were observed. Analysis of
the exhausted dyebaths indicates that thiourea dioxide may be considered as a
more environmental friendly substitute for sodium sulphide during the
application of sulphur dyes.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/
Thiourea Dioxide (Formamidinesulphinic Acid) A New Reducing Agent for Textile
Printing:Thiourea dioxide, an oxidation product of thiourea, is a reducing agent which is
stable both in solid form and in cold aqueous solution. It has a slight acidic
reaction, and acquires full reducing power only when heated in aqueous solution
to about 100°C. This paper briefly describes the chemistry of thiourea dioxide,
and dealB with it as a reducing agent for vat dyes in the direct and discharge
printing of cellulose acetate, silk, and wool. Owing to its acidic properties,
these fibres can be printed with a minimum of degradation and great safety of
production. The new reducing agent has been tried on a practical scale, and
results of trials are demonstrated.
http://www.arkat-usa.org/
Chemoselective
reduction of carbonyl groups of aromatic nitro carbonyl compounds
to the corresponding nitroalcohols using thiourea dioxide:...Thiourea
dioxide (TUDO) or formamidinesulfinic acid (FSA) - a commercially
available reducing agent has vast applications for waste papers
processing,8 wool bleaching,9 the reduction of ferredoxin, cyctochrome
C and methaemoglobin.10 TUDO is also used for the reduction of organosulfur
compounds (sulfylimines, sulfoxides, disulfides);11 for the synthesis
of selenides and tellurides from the corresponding diselenides and
ditellurides under phase transfer catalysis;12 and the deoxygenation
of ��,��-epoxy ketones.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white powder |
|
PURITY
|
99.0%
min
|
|
THIOUREA
|
0.1%
max
|
SULFUR
(AS SO4) |
0.2%
max
|
| MOISTURE |
0.1%
max
|
|
Fe
|
0.003%
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
50kgs
in fiber drum , 16 MT
in a Container |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF THIOUREA
|
Thiourea (also
called Thiocarbamide or Sulfourea) is the diamide of thiocarbonic acid that
resembles urea but contains sulfur instead of oxygen. 'Thio' is a chemical
prefix indicates the replacement of an oxygen in an acid radical by sulfur with
a negative valence of 2; meaning 'Sulfur' derived from the Greek theion. In fact,
thiourea occurs as the mixture of two tautomers: S=C(NH2)2 ( Thiourea) + HS=CNHNH2
(Isothiourea), accordingly, provides three
functional groups (mino, imino, and thiol).
Thiourea is a lustrous
white crystalline compound; estimated melting point is 170-180 C; soluble in
water and in polar organic solvents; insoluble in non-polar solvents. The exact melting point and boiling point are not available since rearrangement
to ammonium thiocyanate (NH4SCN) occurs at about 135 C and decomposition occurs.
It
can be prepared by heating ammonium thiocyanate, or by the addition of hydrogen
sulfide to cyanamide. The latter is the more common method. Thiourea is used
directly in ore filtering, metal refinery and cleaning, isomerization catalyst
(conversion of maleic to fumaric acid) and as an additive in fertilizers to (inhibit the nitrification process), drilling auxiliaries, light-sensitive
photocopy paper and explosives. It is used as a
fixing agent in photography, as a liquefying agent in animal hide glue, as an
insecticide, as a textile-treating agent, and as an intermediate to produce
other compounds. Thiourea and its derivatives are versatile intermediates for the
synthesis of modified thermosetting resins, thiourea dioxide, dyes, flame
retardants, vulcanization accelerators, plant protection agents, pesticides,
amino resins, peptizing agents, fungicides, hair preparations, dry cleaning chemicals, corrosion
inhibitors and
thiazole drugs (e.g., antiseptic, thyrotherapeutic, narcotic, and
tuberculostatic agents).
Dithiobiurea possesses a wide dipole moment and thus is involved in the forming wide metal chelated complexes as the radioactiv-compound which
used in radiopharmaceutical imaging, inhibiting enzyme function, kidney function
study and to treat toxic metal poisoning. It is used in co-crystals development
used in the field of nonlinear optics to generate new coherent wavelengths.
|
